Interface Protocols
Protocols – Uses for communication with devices
Communication are different types
- Intra – Communication between two devices within device
Ex: I2C, SPI
- Inter – Communication between two devices
Ex: CPU & Microcontroller, UART
- Simplex Duplex - One way communication ex: Fm
- Half Duplex - Two-way communication but only receive or transfer at a time ex: walkie talkie
- Full Duplex - Two-way communication at a time ex: Mobile
- Synchronous - Will use clock signal to send or receive any data
- Asynchronous - Need to maintain same frequency while transferring and receiving using clock signal
UART – Universal Asynchronous Receive and Transmitter
- We will transfer data using serial communication
- It will use two wires Rx & Tx
- It is synchronous communication to transfer data
- Parity Bit is used to check whether data is correct or not at receiver end
- Even Parity – No of ‘1’ in data even
- Odd Parity – No of ‘1’ in data odd
- Uses Baud rate of 115200 bps, 96000 bps
Cons:
- When Baud Rate differs will be mismatch in data
- It will used only short-range communications
SPI – Serial Peripheral Interface
It uses Master & Slave terminology and uses parallel communication
- MISO - Master In, Slave Out
- MOSI - Master Out, Slave In
- SCLK - Serial Clk (Always Master generates the clock)
- CS/SS - Chip select/ Slave Select
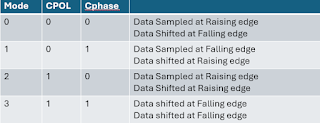
- CPOL - Clock Polarity - Decides data Format
- Cphase - Clock Phase - Decides when bits need to be transferred by tx & when bits need to be received by Rx
We can connect one master to multiple slaves, but we cannot use multiple master
Pros:
- No stop bits & start bits, So data transferred will be faster
- Higher data transfer rate
- Full Duplex
- Without interruption transfer the data
Cons:
- We cannot sure whether data transferred proper or not
- Single master
- No Acknowledgement pin
I2C – Inter Integrated Circuit
- Half duplex communication
- Serial communication
- Synchronous mode
It has unique address
Start – 7 or 10bitaddress – 1 bit read/write – 1bit Ack – 8 bits data – 1bit ack – 8 bits data –– 1bit Ack – 1bit stop




Comments
Post a Comment